Table Of Content
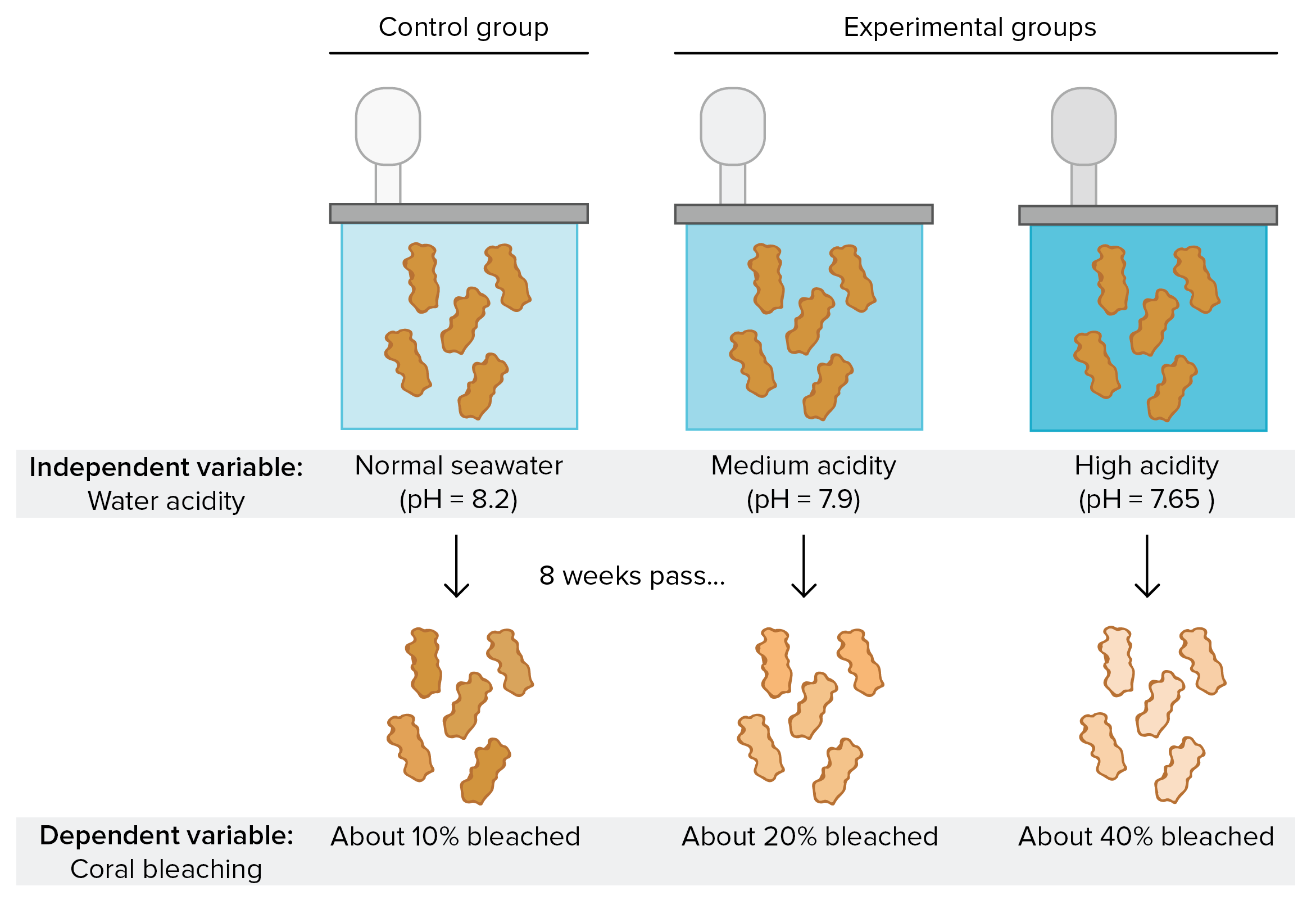
With a firm understanding of the system you intend to study, you can write a specific, testable hypothesis. Researchers assign the first control group a posttest only and the second control group a pretest and a posttest. This structure requires the researcher to divide participants into two random groups. One group receives no stimuli and acts as a control while the other group experiences stimuli. This method includes two or more groups, enabling the researcher to use one group as a control. Various settings and professions can use experimental research to gather information and observe behavior in controlled settings.
Step 2: Write your hypothesis
Quasi-experimental research is more common in educational studies, nursing, or other research projects where it's not ethical or practical to use randomized subject groups. For instance, if the control group also experiences a change, it reveals that taking the test twice changes the results. With the ability to analyze the relationship between variables and using measurable data, you can increase the accuracy of the result. Surveys can be shared with the respondents both physically and electronically. When collecting data through surveys, the kind of data collected depends on the respondent, and researchers have limited control over it. Data collection methods in experimental research are the different ways in which data can be collected for experimental research.
Methods
For many designed studies, the sample size is an integer multiple of the total number of treatments. This integer is the number of times each treatment being repeated and one complete repitition of all treatments (under similar experimental conditions) is called a complete replicate of the experiment. Interventional studies are experiments where the researcher actively performs an intervention in some or all members of a group of participants. This intervention could take many forms – for example, administration of a drug or vaccine, performance of a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure, and introduction of an educational tool.
Experimental Studies
It is less expensive and less time‐consuming than cohort studies (described in section “Cohort study”). An example of a case‐control study was performed in Pakistan evaluating the risk factors for neonatal tetanus. They retrospectively reviewed a defined cohort for cases with and without neonatal tetanus.9 They found a strong association of the application of ghee (clarified butter) as a risk factor for neonatal tetanus.
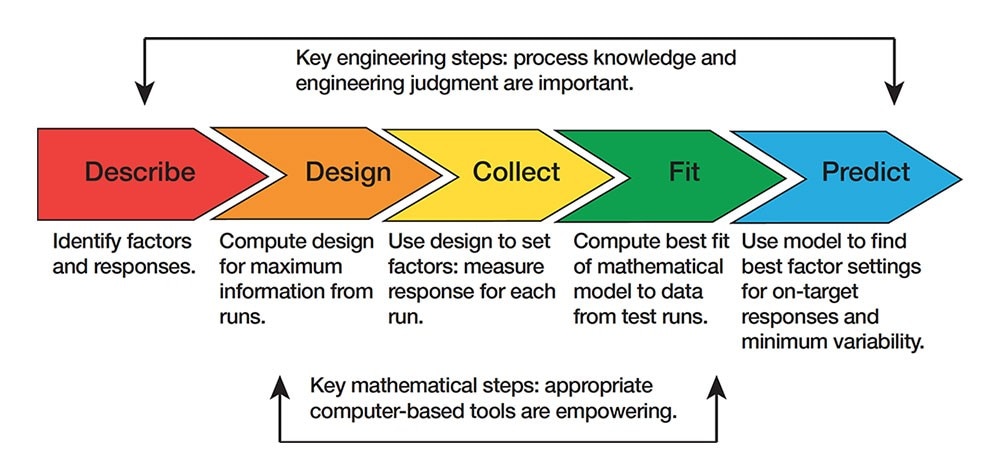
This also ensures comparability between groups as most baseline characteristics are similar prior to randomization and therefore helps to interpret the results regarding the intervention/experiment group without bias. Experimental design provides a structured approach to designing and conducting experiments, ensuring that the results are reliable and valid. The purpose of experimental design is to control and manipulate one or more independent variables to determine their effect on a dependent variable. Experimental design allows researchers to systematically investigate causal relationships between variables, and to establish cause-and-effect relationships between the independent and dependent variables. Through experimental design, researchers can test hypotheses and make inferences about the population from which the sample was drawn.
The pre-experimental design will help researchers understand whether further investigation is necessary for the groups under observation. Research study designs are of many types, each with its advantages and limitations. The type of study design used to answer a particular research question is determined by the nature of question, the goal of research, and the availability of resources. Since the design of a study can affect the validity of its results, it is important to understand the different types of study designs and their strengths and limitations. Repeated Measures design is an experimental design where the same participants participate in each independent variable condition.
What factors will affect the effectiveness of using ChatGPT to solve programming problems? A quasi-experimental ... - Nature.com
What factors will affect the effectiveness of using ChatGPT to solve programming problems? A quasi-experimental ....
Posted: Mon, 26 Feb 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Analytical Studies
Typically, subjects with the disease tend to remember certain events compared to subjects without the disease. One of the ways to decrease observer bias is to use blinding (discussed in section “Blinding”). Experimental research design is a framework of protocols and procedures created to conduct experimental research with a scientific approach using two sets of variables.
Prospective versus retrospective study designs
The purpose of study, experimental, or research design in scientific manuscripts has changed significantly over the years. It has evolved from an explanation of the design of the experiment (ie, data gathering or acquisition) to an explanation of the statistical analysis. However, these differences will need to be accounted during analysis of results. Experimental research is often the final form of a study conducted in the research process which is considered to provide conclusive and specific results.
Experimental Research Design Types
There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data. This involves randomly assigning participants to different groups or treatments to ensure that any observed differences between groups are due to the treatment and not to other factors. Similarly, experimental research is used in the field of psychology to test theories and understand human behavior. By manipulating variables such as stimuli, researchers can gain insights into how the brain works and identify new treatment options for mental health disorders. You should be able to create groups with an equal number of subjects and include subjects that match your target audience.
Experimental research is a study conducted with a scientific approach using two sets of variables. The first set acts as a constant, which you use to measure the differences of the second set. Quasi-experimental research design doesn’t have randomly selected participants. Researchers typically divide the groups in this research by pre-existing differences.
It is the most accurate type of experimental design and may be carried out with or without a pretest on at least 2 randomly assigned dependent subjects. A non‐randomized clinical trial involves an approach to selecting controls without randomization. With this type of study design a pattern is usually adopted, such as, selection of subjects and controls on certain days of the week. Depending on the approach adopted, the selection of subjects becomes predictable and therefore, there is bias with regards to selection of subjects and controls that would question the validity of the results obtained. Descriptive observational studies provide a description of the exposure and/or the outcome, and analytic observational studies provide a measurement of the association between the exposure and the outcome.
Study design is the preferred term in the AMA Manual of Style,2 so I will use it here. We have discussed various clinical research study designs in this comprehensive review. Though there are various designs available, one must consider various ethical aspects of the study. Hence, each study will require thorough review of the protocol by the institutional review board before approval and implementation. Information bias is when a systematic error is committed while obtaining data from the study subjects. This can be in the form of recall bias when subject is required to remember certain events from the past.
If you don’t have enough data to support your decisions, you must first determine the facts. When groups experience different product designs, the company can assess which option most appeals to potential customers. Experimental research may not capture the complexity of some phenomena, such as social interactions or cultural norms.
Randomly allocating participants to independent variable conditions means that all participants should have an equal chance of taking part in each condition. A matched pairs design is an experimental design where pairs of participants are matched in terms of key variables, such as age or socioeconomic status. One member of each pair is then placed into the experimental group and the other member into the control group. The purpose of this Communications article is to clarify the purpose and placement of study design elements in an experimental manuscript.
No comments:
Post a Comment